Insect structure
External morphology of insects
Segmented composition is the biggest
characteristic of insects, and the skin between segments is soft and
folded inward in a membranous form. Insect body segments are divided
into four sections, tergum, sternum, and laterotergites, and their
bodies are divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
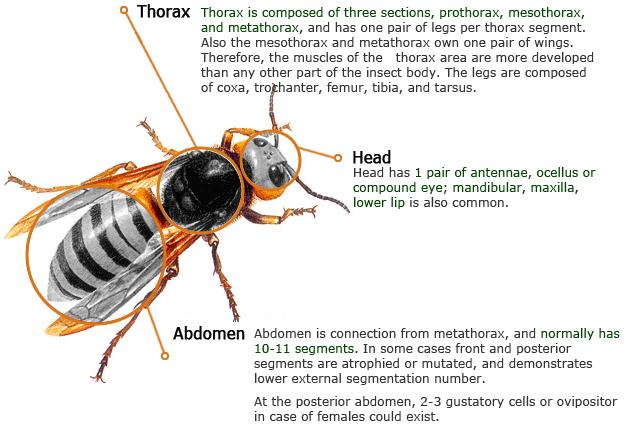
- Thorax
-
The thorax is composed of three sections: prothorax,
mesothorax, and metathorax, each of which has one pair of legs.
Also, the mesothorax and metathorax each have one pair of wings.
Therefore, the muscles of the thorax are more developed than any
other part of the insect body. Their legs are composed of five
segments: coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, and tarsus.
- Abdomen
-
Insect abdomens are connected to the metathorax, and
normally composed of 10 or 11 segments. There are some cases where
some front and posterior segments are atrophied or transformed to
show a smaller number of external segments. In some cases, the
posterior abdomen has two or three caudal legs, and the female often
has an ovipositor.
- Head
-
In general, insect heads have one pair of antennae, three
ocelli and compound eyes, a mandible, a maxilla, and a lower lip.
Insect characteristics
Insect is a large group of more than 850,000
species and accounts for at least 3/4 of the entire animal kingdom.
They have various morphological characteristics, which are organized
as follows.
- The body is divided into head, thorax, and abdomen, and the head has one pair of antennae and specifically developed gnathal segment.
- Insects differ from other animals in having an exoskeleton.
- Insect abdomens are composed of 11 segments during the larva stage, and the appendage disappears when the insect becomes an imago.
- The body is bisymmetric.
- Insects have an open circulatory system.
- Their digestive system is composed of three parts: foregut, mid-gut, and hindgut, and there is a malpighian tubule at the end of hindgut.
- They breathe through their trachea and spiracle.
- In general, males and females are separated.

 Korea Biodiversity Information System > Insect Resource > Insect Classes > Insect Structure
Korea Biodiversity Information System > Insect Resource > Insect Classes > Insect Structure
